Bleaching Hair

A: Hair bleaching is used when you want to lighten your hair significantly, especially when going from a darker shade to a much lighter one.
Bleaching, also known as decolorizing or lightening, is a chemical process that lightens hair by breaking down the natural or artificial color molecules within the hair shaft. This transformation involves complex chemistry, and careful application is essential to achieve the desired results while minimizing damage.
• Eumelanin, which produces brown and black pigments.
• Pheomelanin, which produces red and yellow pigments.
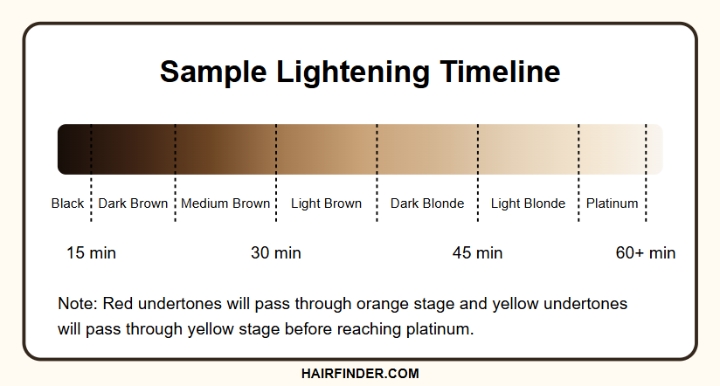
Pheomelanin is more resistant to bleaching, which is why hair often appears brassy or yellow during the process before reaching pale or platinum blonde tones.
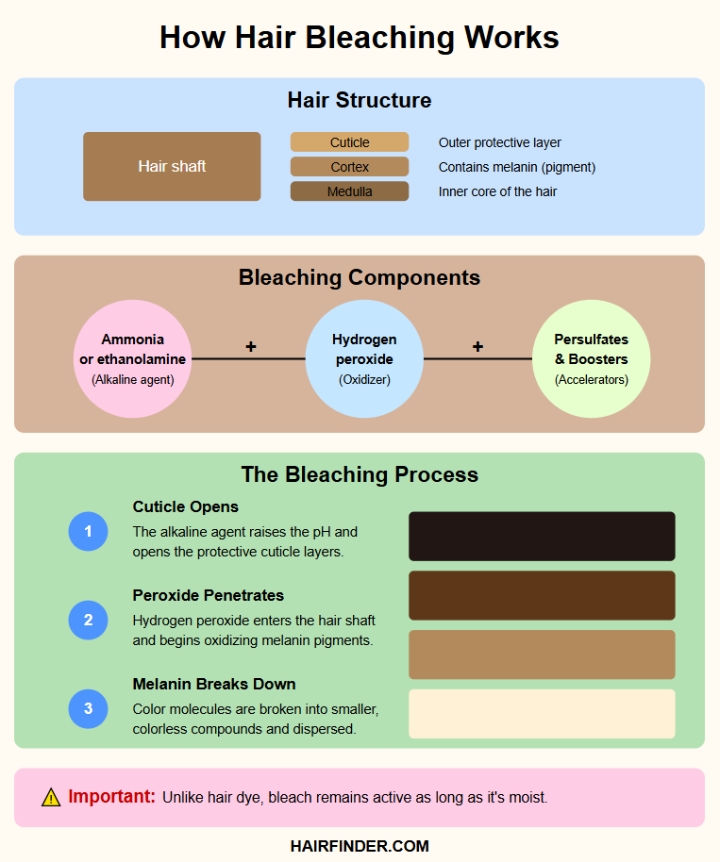
1. Alkaline Agent. Usually ammonia or ethanolamine. It opens the cuticle (the hair's outer protective layer) and softens the cortex, the middle layer where pigment resides. This allows the bleach to penetrate the hair shaft.
2. Oxidizing Agent. Typically hydrogen peroxide. It enters the cortex and breaks down melanin through oxidation, transforming the colored pigment molecules into smaller, colorless compounds.
The actual bleaching process includes several stages:
1. Cuticle Opening: The alkaline agent raises the hair's pH, lifting the cuticle scales to allow chemical penetration.
2. Cortex Penetration: Hydrogen peroxide reaches the cortex, where melanin is stored.
3. Oxidation Reaction: Peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen. The released oxygen disrupts the melanin’s chemical bonds, breaking the pigment apart.
4. Melanin Dispersal: The broken-down melanin, now colorless, becomes small enough to be partially rinsed out of the hair shaft.
To maintain hair health, proper preparation, precise application, and diligent aftercare are essential. For best results, and to avoid significant damage, professional application is strongly recommended. Bleaching is not without risks and is generally not something to attempt at home.
©hairfinder.com
See also:
Hair bleaching problems
Hair color level and peroxide developer
Where does the color go when you bleach dark hair?
How can I remove bleach from my hair?